The organization¶
The City of Boston regularly inspects every restaurant to monitor and improve food safety and public health.
The challenge¶
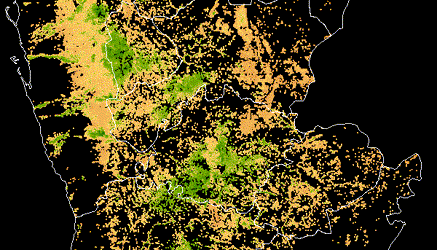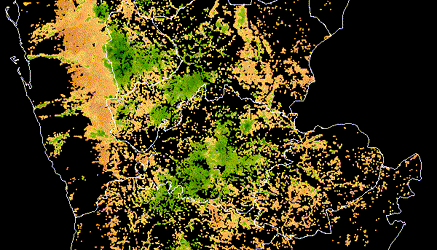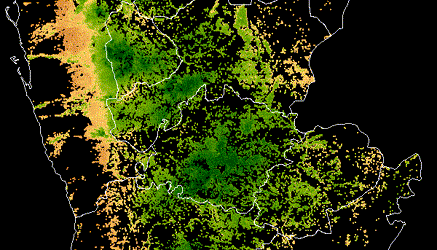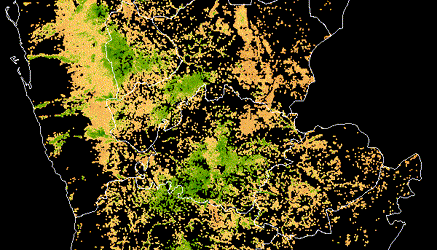
As in most cities, health inspections are generally random, which can increase time spent on spot checks at clean restaurants that have been following the rules closely — and missed opportunities to improve health and hygiene at places with more pressing food safety issues. Meanwhile, each year, millions of people cycle through and post Yelp reviews about their experiences at these same restaurants. The information in these reviews has the potential to improve the City’s inspection efforts, and could transform the way inspections are targeted.
The approach¶
DrivenData, in partnership with Yelp and Harvard, and with support from the City of Boston, structured a predictive challenge to tie Yelp reviews and ratings with the results of Boston’s hygiene inspections. The goal was to use data from social media to narrow the search for health code violations in Boston, pulling out the words, phrases, ratings, and patterns that predict violations to help public health inspectors do their jobs more effectively.
Modelers with the top-performing approaches made predictions for where minor, major, and severe hygiene violations would surface for 6 weeks into the future. Over that time, DrivenData compared their predictions with what public health inspectors actually found when they went into restaurants. At the end of the evaluation period, we saw which teams had developed the most accurate predictions.
The results¶
The competition results were studied by Harvard researcher Mike Luca and covered in the Washington Post in 2015: "Using the winning algorithm, Luca says, Boston could catch the same number of health violations with 40 percent fewer inspections, simply by better targeting city resources at what appear to be dirty-kitchen hotspots. The city of Boston is now considering ways to use such a model."
And in fact they have. As of 2017, the city of Boston used the top algorithms from this project and - in practice - found 25% more health violations, while also surfacing around 60% of the most critical violations earlier than before. By taking advantage of past data and combining with new sources of information, the city can catch public health risks sooner and get a smarter view of how to dedicate scarce public resources.